What Is a Nursing Diagnosis?
A nursing diagnosis is a part of the nursing process and is a clinical judgment that a bedside nurse determines the plan of care for the patients. These diagnoses allow the nurse to perform possible interventions for the patient, family, and community. They are developed with thoughtful consideration of a patient’s physical assessment and can help measure outcomes for the nursing care plan.
History of Nursing Diagnoses
- 1973: The first conference to identify nursing knowledge and a classification system; NANDA was founded
- 1977: First Canadian Conference takes place in Toronto
- 1982: NANDA formed with members from the United States and Canada
- 1984: NANDA established a Diagnosis Review Committee
- 1987: American Nurses Association (ANA) officially recognizes NANDA to govern the development of a classification system for nursing diagnosis
- 1987: International Nursing Conference held in Alberta, Canada
- 1990: 9th NANDA conference and the official definition of the nursing diagnosis established
- 1997: Official journal renamed from “Nursing Diagnosis” to “Nursing Diagnosis: The International Journal of Nursing Terminologies and Classifications”
- 2002: NANDA changes to NANDA International (NANDA-I) and Taxonomy II released
- 2020: 244 NANDA-I approved diagnosis
NANDA Classification of Nursing Diagnoses
NANDA-I adopted the Taxonomy II after consideration and collaboration with the National Library of Medicine (NLM) in regard to healthcare terminology codes. Taxonomy II has three levels: domains, classes, and nursing diagnoses.
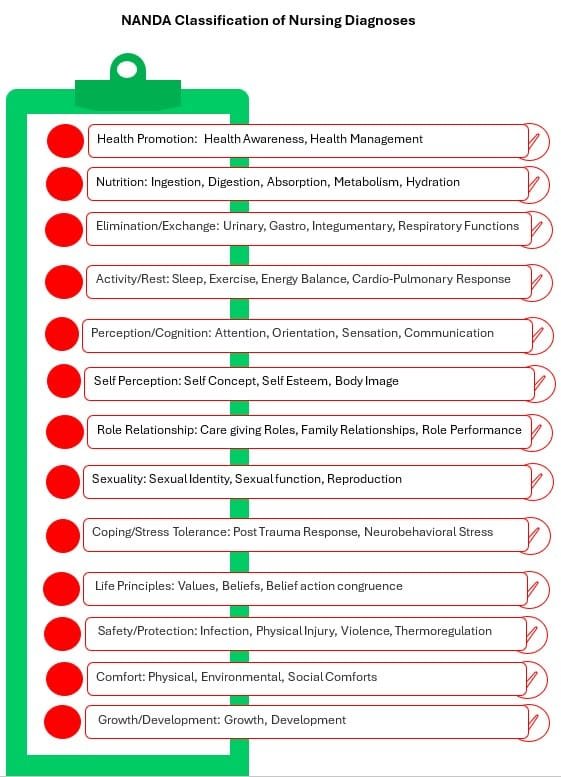
There are currently 13 domains and 47 classes:
- Domain 1 – Health Promotion
- Health Awareness
- Health Management
- Domain 2 – Nutrition
- Ingestion
- Digestion
- Absorption
- Metabolism
- Hydration
- Domain 3 – Elimination/Exchange
- Urinary Function
- Gastrointestinal Function
- Integumentary Function
- Respiratory Function
- Domain 4 – Activity/Rest
- Sleep/Rest
- Activity/Exercise
- Energy Balance
- Cardiovascular-Pulmonary Responses
- Self Care
- Domain 5 – Perception/Cognition
- Attention
- Orientation
- Sensation/Perception
- Cognition
- Communication
- Domain 6 – Self-Perception
- Self-concept
- Self-esteem
- Body image
- Domain 7 – Role Relationship
- Caregiving Roles
- Family Relationships
- Role Performance
- Domain 8 – Sexuality
- Sexual Identity
- Sexual Function
- Reproduction
- Domain 9 – Coping/Stress Tolerance
- Post-trauma Responses
- Coping Response
- Neuro-Behavioral Stress
- Development
- Domain 10 – Life Principles
- Values
- Beliefs
- Value/Belief Action Congruence
- Domain 11 – Safety/Protection
- Infection
- Physical Injury
- Violence
- Environmental Hazards
- Defensive Processes
- Thermoregulation
- Domain 12 – Comfort
- Physical Comfort
- Environmental Comfort
- Social Comfort
- Domain 13 – Growth/Development
- Growth
- Development
NANDA Nursing Diagnosis List
A nursing diagnosis is a professional judgment based on the application of clinical knowledge which determines potential or actual experiences and responses to health problems and life processes. The list of NANDA nursing diagnosis can be applied to individuals, families or communities. Included with the list of NANDA nursing diagnosis is an array of commonly applied interventions from which the caregiver can choose to implement to the given patient.
The NANDA Diagnosis List is Categorised in the Following Headings

Problem-focused and risk diagnoses are the most difficult nursing diagnoses to write because they have multiple parts. According to NANDA-I, the simplest ways to write these nursing diagnoses are as follows:
PROBLEM-FOCUSED DIAGNOSIS
Problem-Focused Diagnosis related to ………………………………………………………………. (Related Factors) as evidenced by………………………………………………………………………….
RISK DIAGNOSIS
The correct statement for a NANDA-I nursing diagnosis would be Risk for …………………………………. as evidenced by………………………………………………….(Risk Factors).
NANDA Nursing Diagnosis Types
There are 4 types of nursing diagnoses according to NANDA-I. They are:
- Problem- focused
- Risk
- Health promotion
- Syndrome
1. Problem-focused diagnosis
A patient problem present during a nursing assessment is known as a problem-focused diagnosis. Generally, the problem is seen throughout several shifts or a patient’s entire hospitalization. However, depending on the nursing and medical care, it may be resolved during a shift.
Problem-focused diagnoses have three components.
- Nursing diagnosis
- Related factors
- Defining characteristics
Examples of this type of nursing diagnosis include:
- Decreased cardiac output
- Chronic functional constipation
- Impaired gas exchange
Problem-focused nursing diagnoses are typically based on signs and symptoms present in the patient. They are the most common nursing diagnoses and the easiest to identify.
2. Risk Nursing Diagnosis
A risk nursing diagnosis applies when risk factors require intervention from the nurse and healthcare team prior to a real problem developing.
Examples of this type of nursing diagnosis include:
- Risk for imbalanced fluid volume
- Risk for ineffective childbearing process
- Risk for impaired oral mucous membrane integrity
This type of diagnosis often requires clinical reasoning and nursing judgment.
3. Health Promotion Diagnosis
The goal of a health promotion nursing diagnosis is to improve the overall well-being of an individual, family, or community.
Examples of this type of nursing diagnosis include:
- Readiness for enhanced family processes
- Readiness for enhanced hope
- Sedentary lifestyle
4. Syndrome Nursing Diagnosis
A syndrome diagnosis refers to a cluster of nursing diagnoses that occur in a pattern or can all be addressed through the same or similar nursing interventions.
Examples of this diagnosis include:
- Decreased cardiac output
- Decreased cardiac tissue perfusion
- Ineffective cerebral tissue perfusion
- Ineffective peripheral tissue perfusion
Nursing Diagnosis Components
The three main components of a nursing diagnosis are:
- Problem and its definition
- Etiology or risk factors
- Defining characteristics or risk factors
1. The problem statement explains the patient’s current health problem and the nursing interventions needed to care for the patient.
2. Etiology, or related factors, describes the possible reasons for the problem or the conditions in which it developed. These related factors guide the appropriate nursing interventions.
3. Finally, defining characteristics are signs and symptoms that allow for applying a specific diagnostic label. Risk factors are used in place of defining characteristics for risk nursing diagnosis. They refer to factors that increase the patient’s vulnerability to health problems.
Nursing Diagnosis vs Medical Diagnosis
While all important, nursing diagnoses are primarily handled through specific nursing interventions, while medical diagnoses are made by a physician or advanced healthcare practitioner.
The nursing diagnosis can be mental, spiritual, psychosocial, and/or physical. It focuses on the overall care of the patient while the medical diagnosis involves the medical aspect of the patient’s condition.
A medical diagnosis does not change if the condition is resolved, and it remains part of the patient’s health history forever. A nursing diagnosis, however, generally refers to a specific period of time.
Examples of medical diagnosis include:
- Arthritis
- Congestive Heart Failure
- Diabetes Insipidus
- Meningitis
- Scoliosis
- Stroke
REFERENCES
- NANDA International Nursing Diagnoses 2024-2026 Update, 13th Edition, Thieme Medical Publishers, Inc.
- Ernstmeyer K, Christman E, editors. Nursing Fundamentals [Internet]. Eau Claire (WI): Chippewa Valley Technical College; 2021. Appendix A: Sample NANDA-I Diagnoses. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK591814/
- Herdman, T. H., & Kamitsuru, S. (Eds.). (2018). Nursing diagnoses: Definitions and classification, 2018-2020. Thieme Publishers New York
Stories are the threads that bind us; through them, we understand each other, grow, and heal.
JOHN NOORD
Connect with “Nurses Lab Editorial Team”
I hope you found this information helpful. Do you have any questions or comments? Kindly write in comments section. Subscribe the Blog with your email so you can stay updated on upcoming events and the latest articles.





