What is a walker?
A walker is a mobility aid designed to assist individuals who have difficulty walking due to injury, illness, or physical limitations. It typically consists of a lightweight frame with four legs, sometimes equipped with wheels, and provides stability and support to users as they move. In this topic How to Use a Walker to walk is explained in detail.

Walkers are commonly used by elderly individuals, patients recovering from surgery, or those with conditions like arthritis or balance disorders. Some walkers include additional features like brakes, seats, or storage compartments for added convenience.
Indications
- Recovering from an injury to your leg, ankle, foot, hip or back.
- Rehabilitation after surgery or an illness that immobilized you.
- Relearning to walk after temporary or partial paralysis.
- Musculoskeletal conditions that affect your posture and mobility, like arthritis or scoliosis.
- Neurological conditions that affect your coordination and muscle strength, like Parkinson’s or MS.
- Cardiopulmonary (heart and lung) conditions that affect your tolerance for exercise.
- Needing help bearing your own weight.
- Needing help with balance and staying upright.
Types of walkers
The standard walker (also called a Zimmer frame or pulpit frame) comes in two variations. These are the walkers that healthcare facilities typically provide. They’re generally intended for limited, indoor use.
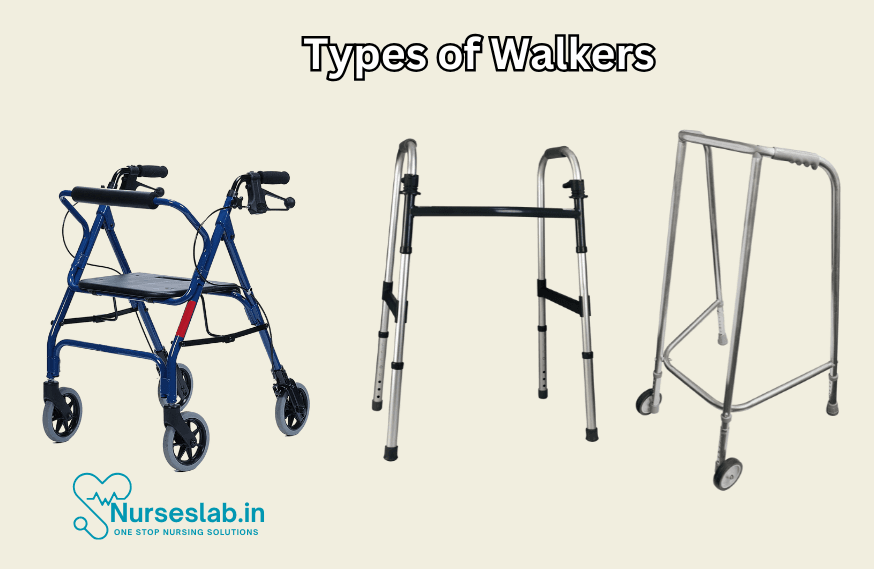
There are also several specialized types of walkers designed for more specific uses. Your healthcare provider might recommend a more specialized walker for you based on your condition and needs.
1.Four-point walker
The standard “four-point” walker has four rubber-tipped feet. You lift the walker and step forward with it, following with your feet. This model provides the most stability for people with balance issues.
2.Two-wheeled walker
The two-wheeled walker has wheels on the front two feet and rubber tips on the back two feet. Instead of lifting this walker to take a step, you slide it forward. This allows for a more natural walking pattern.
Specialized walkers
Beyond the basic models, there are some specialized types of walkers, including:
- Rollators: An all-wheeled walker, also called a mobile walker or rollator, is an alternative mobility aid that you can use outdoors or to go shopping. It has three or four larger wheels with brakes for traversing uneven terrain. They often have storage and a seat for rest breaks.
- Forearm support walker: Also called a platform walker, upright walker or gutter frame, this walker allows you to bear weight on your forearms instead of your wrists. A padded “gutter” supports your forearms, positioned at 90 degrees. The walker may have two or four wheels.
- Reverse walker: A reverse or posterior walker is a four-wheeled frame that you pull behind you rather than pushing in front of you. You hold the frame at the sides of your hips rather than in front. This option provides more posture support and stability if you tend to tip backward.
- Knee walker: A knee walker is a specialized walker that you use when you can’t walk on one foot. It’s usually a short-term solution. The walker has four wheels and a platform that you rest your knee on. You push yourself along with the other foot while holding onto the handlebars.
Accessories
Walkers can be customized with various accessories to enhance their functionality, comfort, and convenience. Here are some popular walker accessories:
1. Storage Solutions
- Walker baskets: Ideal for carrying personal items like books, groceries, or medical supplies.
- Walker bags or pouches: Attach to the frame for secure storage of smaller items.
2. Mobility Enhancements
- Walker glides or skis: Help the walker move smoothly over surfaces.
- Tennis balls: Pre-cut tennis balls can be added to the legs for easier movement.
- Wheels: Convert a standard walker into a rolling walker for increased mobility.
3. Comfort Features
- Hand grips: Cushioned or ergonomic grips to reduce hand strain.
- Seat attachments: Provide a resting spot for users during longer walks.
4. Convenience Add-Ons
- Cup holders: Securely hold water bottles, coffee cups, or other beverages.
- Trays: Allow users to carry meals or other items hands-free.
5. Safety Accessories
- Brakes: Add control for walkers with wheels.
- Lights or reflectors: Improve visibility in low-light conditions.
How do you walk with a walker
Walking with a walker involves proper technique to ensure safety and maximize its effectiveness. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
1. Positioning the Walker
- Stand inside the walker, holding onto the handles with both hands.
- Ensure the walker is at the correct height—your elbows should be slightly bent when gripping the handles.
2. Moving the Walker
- Push the walker forward about one step ahead, keeping all four legs or wheels on the ground.
- Avoid moving the walker too far ahead; it should remain within arm’s reach.
3. Taking Steps
- Step into the walker, starting with your weaker leg (if applicable).
- Bring your stronger leg forward to meet the weaker leg, keeping your weight supported by the walker.
4. Maintaining Balance
- Keep your weight centered as you move forward.
- Avoid leaning too far forward or sideways, as this can affect balance and stability.
5. Repeat
- Continue moving the walker forward and stepping into it, alternating your legs.
Safety Tips
- Take your time and move at a comfortable pace—don’t rush.
- Ensure the walker is on a level surface to prevent tipping or slipping.
- Check the walker for loose parts or damage before each use.
Benefits of using a walker
Using a walker offers numerous benefits, especially for individuals with mobility challenges. Here are some key advantages:
- Walkers provide additional support, reducing the risk of falls and improving confidence while walking.
- They allow individuals to move around more freely, enabling them to maintain independence and participate in daily activities.
- Walkers help distribute weight, alleviating pressure on joints and muscles, which is particularly beneficial for those with arthritis or injuries.
- By offering support, walkers enable users to walk longer distances without tiring as quickly.
- Many walkers come with features like brakes, seats, and storage compartments, making them practical for various needs.
- Walkers are often used in physical therapy to aid recovery from surgeries or injuries, promoting gradual and safe mobility improvement.
Dos of Using Walker
Using a walker correctly can enhance mobility and prevent injuries. Here are some important “dos” to follow:
- Do ensure the walker is at the correct height—handles should align with your wrist crease when standing upright.
- Do check that the walker is stable and secure before use.
- Do stand upright and avoid leaning too far forward or backward.
- Do keep your elbows slightly bent while gripping the handles.
- Do move the walker one step ahead before stepping forward.
- Do step into the walker rather than behind it for better balance.
- Do take small, steady steps to maintain control.
- Do use the walker on flat, even surfaces to prevent tipping.
- Do check for loose screws or worn-out grips regularly.
- Do use non-slip rubber tips or wheels suited for your environment.
- Do use walker baskets or pouches for carrying essentials.
- Do consider hand grips or padding for extra comfort.
- Do consult a physical therapist for proper walker use and adjustments.
- Do practice walking techniques under supervision if needed.
Don’ts of Using Walker
Using a walker incorrectly can lead to discomfort or even injuries. Here are some important “don’ts” to keep in mind:
- Don’t use a walker that is too high or too low—it should align with your wrist crease when standing upright.
- Don’t hunch over or strain your shoulders while using the walker.
- Don’t push the walker too far ahead—it should remain within arm’s reach for stability.
- Don’t step too far forward before moving the walker; always step into the walker’s frame.
- Don’t use the walker on uneven, slippery, or cluttered surfaces without proper precautions.
- Don’t attempt to use a walker on stairs unless it is specifically designed for that purpose.
- Don’t hang heavy bags or items on the walker, as this can affect balance and stability.
- Don’t use the walker as a seat unless it has a built-in seat designed for sitting.
- Don’t neglect regular inspections—check for loose screws, worn-out grips, or damaged parts.
- Don’t use a walker with unstable or broken components, as it can increase the risk of falls.
- Don’t grip the walker too tightly—this can cause unnecessary strain on your hands and wrists.
- Don’t lean too far forward or sideways, as this can affect balance and posture.
How to maintain a Walker
Proper maintenance of your walker ensures its longevity and functionality:
| Maintenance Task | Description | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Check Wheel Condition (for rolling walkers) | Inspect wheels for wear or damage; ensure they roll smoothly. | Weekly |
| Tighten Screws & Bolts | Ensure all screws and bolts are secure to prevent wobbling. | Monthly |
| Cleansing Frame & Handles | Wipe down surfaces with disinfectant wipes regularly. | As needed |
| Check Weight Limit Compliance | If weight changes occur, reassess if current walker meets new needs. | As needed |
REFERENCES
- Elsevier. How To Use A Walker (https://elsevier.health/en-US/preview/how-to-use-walker). Updated 9/17/2021.
- Physiopedia. Walkers (https://www.physio-pedia.com/Walkers).
- How to use crutches, canes, and walkers. American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/topic.cfm?topic=A00181.
- Health Education & Content Services. Using a walker (weight bearing). Mayo Clinic; 2017.
- Webster JB, et al., eds. Canes, crutches, and walkers. In: Atlas of Orthoses and Assistive Devices. 5th ed. Elsevier; 2019. https://www.clinicalkey.com.
- U.S. National Library of Medicine. Using a walker. https://medlineplus.gov/ency/patientinstructions/000342.html. Updated 4/27/2023.
Stories are the threads that bind us; through them, we understand each other, grow, and heal.
JOHN NOORD
Connect with “Nurses Lab Editorial Team”
I hope you found this information helpful. Do you have any questions or comments? Kindly write in comments section. Subscribe the Blog with your email so you can stay updated on upcoming events an






